Uterine fibroids are growths made of smooth muscle cells, fibroblasts, and other material that grow in or on the wall of the uterus.
Fibroids may grow as a single tumor or in clusters. In many cases, a single uterus contains many fibroids.
Fibroids can be different sizes or shapes.1 Bunches or clusters of fibroids are often of different sizes. Fibroids can grow, shrink, or remain a constant size over time.2
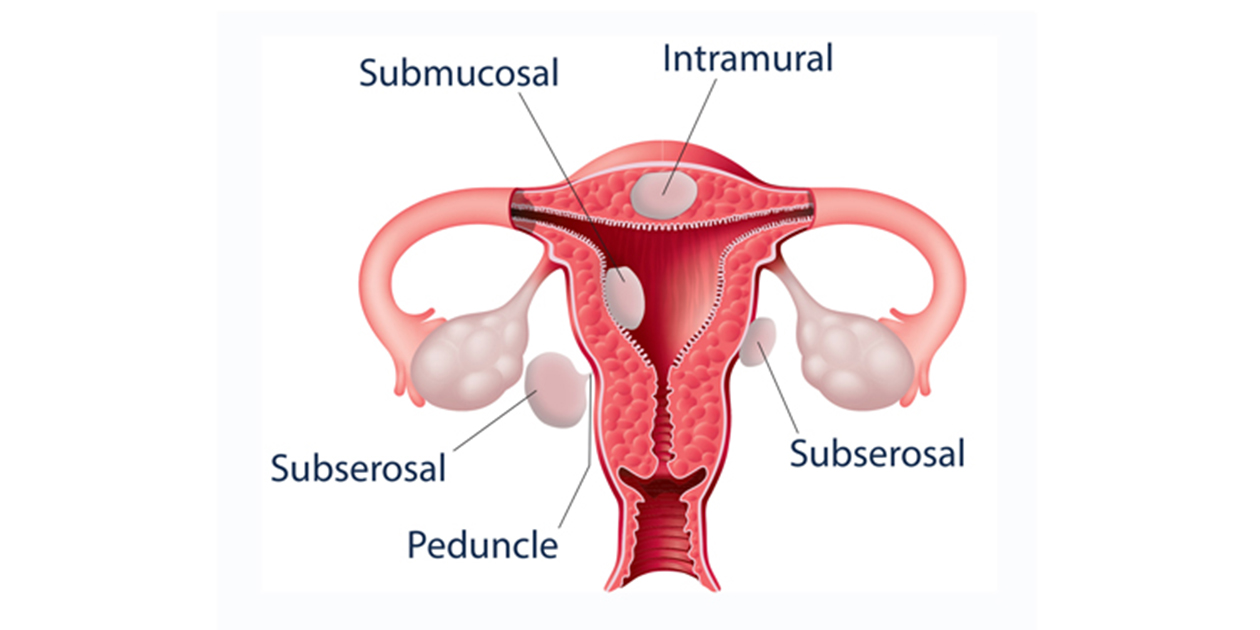
Health care providers categorize fibroids based on where they grow:
- Submucosal (pronounced sub-myoo-KOH-sul) fibroids grow just underneath the uterine lining and into the endometrial cavity.
- Intramural (pronounced in-tra-MYUR-ul) fibroids grow in between the muscles of the uterus.
- Subserosal (pronounced sub-sur-OH-sul) fibroids grow on the outside of the uterus.
Some fibroids grow on stalks that grow out from the surface of the uterus or into the uterine cavity. These are called pedunculated (pronounced ped-UN-kyoo-lay-ted) fibroids.


 BACK TO TOP
BACK TO TOP