Stroke is a leading cause of disability and death in the United States. Strokes leave many people with long-term physical and cognitive difficulties; rehabilitation after stroke is an important goal.
NICHD is one of many federal agencies and NIH Institutes working to understand stroke and how to improve methods of post-stroke rehabilitation.
General Information
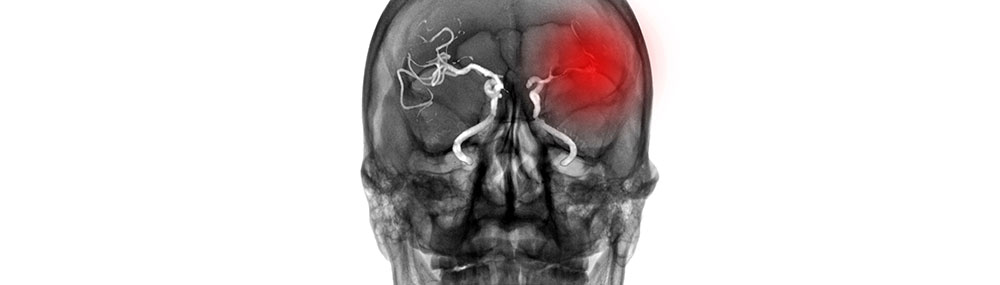
A stroke occurs when a blocked vessel or artery prevents blood from getting to part of the brain, or when a vessel or artery bursts and spills blood into the brain.
Stroke symptoms come on suddenly and include numbness or weakness of the face, arm, or leg; confusion or trouble talking; dizziness and vision problems.
Each year, about 795,000 people in the United States have strokes, and of these incidents, 137,000 of the people die.
Ischemic stroke—the most common kind of stroke—is caused by a blockage in an artery carrying blood to the brain.
At the hospital, healthcare providers will treat stroke with medications, surgery, or both, depending on the type of stroke. Recovery may take months or years.
Research
NICHD conducts and supports research on stroke and on many disorders associated with it.
Find a Study
NICHD conducts and supports a variety of clinical research projects related to stroke.
More Information
Find answers to other common questions about stroke, such as whether stroke is preventable.
 BACK TO TOP
BACK TO TOP