TBI symptoms vary depending on:
- The type of injury
- How severe the injury is
- What area of the brain is injured
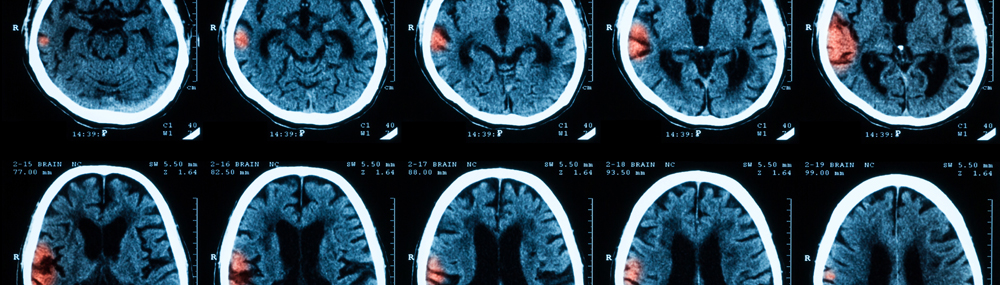
TBI injuries can be both local (the exact place on the brain where the injury occurred) and include the surrounding tissues, which can also be affected by the damage to the initial site. This means that some symptoms appear right away, while others may appear several days or even weeks later and evolve over time. A person with TBI may or may not lose consciousness. Loss of consciousness, sometimes called a blackout, does not necessarily mean the TBI is severe, especially if the blackout lasts for only a short time. Learn about treatments for TBI.
 BACK TO TOP
BACK TO TOP