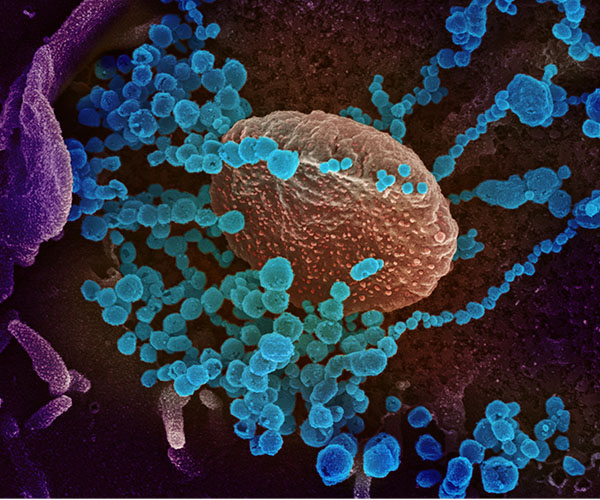
Identifying a Potential COVID-19 Drug
Although the COVID-19 vaccines authorized in the United States are highly effective at preventing serious disease and death, vaccination rates remain low in certain areas of the country, and viral variants with reduced sensitivity to vaccines may continue to emerge. Developing safe and effective oral antiviral medications can address these gaps and further reduce both disease and spread of the COVID-19 virus.
Read about work from the Rouault Lab that identifies a potential oral antiviral drug for COVID-19.
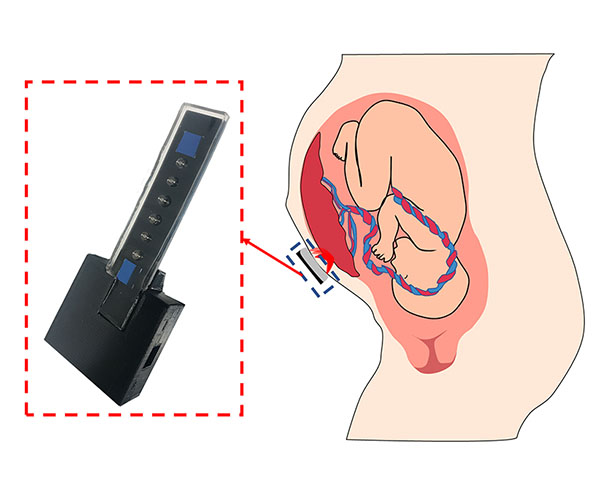
Monitoring Placental Health During Pregnancy
The placenta plays critical roles in fetal development, pregnancy outcomes, and lifelong health. A non-invasive, easy-to-use method to monitor the oxygen level of the placenta during pregnancy would be a useful tool for assessing maternal and fetal health.
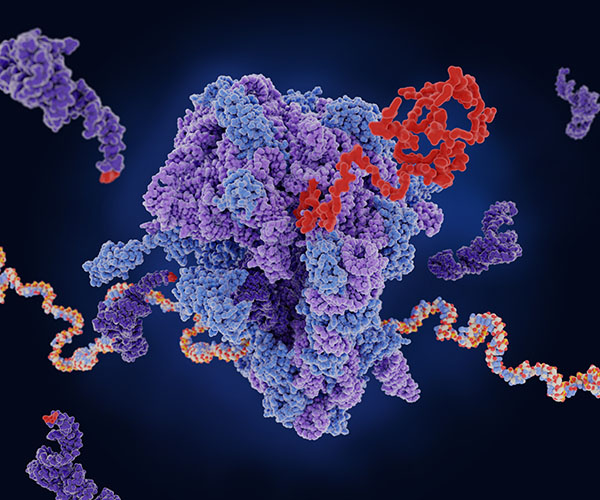
Revising Our Understanding of Polymerase III
RNA synthesis, or transcription, is a fundamental process that transcribes DNA instructions into RNA molecules. These RNAs can be messenger RNAs that are translated into proteins, or they can be non-coding RNAs that carry out other functions in a cell. Transcription is a tightly regulated process that involves enzymes called polymerases.

Identifying Mutations in Neuroendocrine Tumors
Pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma are rare neuroendocrine tumors that can be hard to treat. Discovering genetic mutations that cause this type of cancer can help researchers develop more effective treatments.
Read about work from the Pacak Lab that identified mutations in a gene for succinyl-CoA ligase.
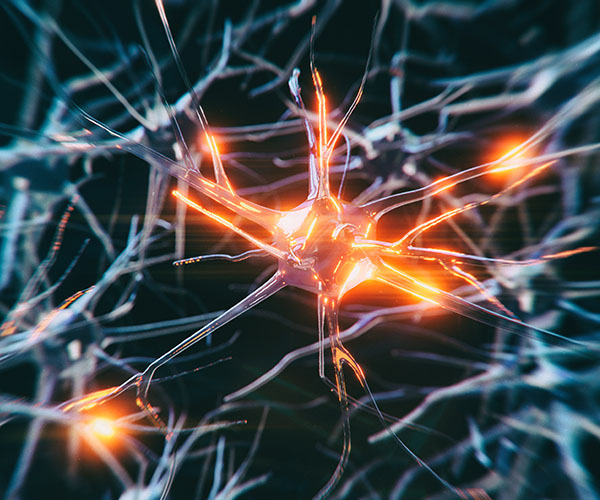
Mapping Interneurons to Understand the Development of Mental Health Disorders
GABAergic inhibitory interneurons are increasingly considered a central component in the development of mental health disorders. These neurons help shape diverse aspects of brain circuit maturation and regulate information processing, especially among children and adolescents, whose brains are still developing.
Understanding the Regulation and Transport of Polyamines
Polyamines are small organic compounds that are essential for cellular growth. They’re produced by the body and also found in certain foods. Despite their importance, how cells take up polyamines is not well known.
Read about work from the Dever and Banerjee Labs that identifies a polyamine transporter in yeast.
Discovering Evolutionary Drivers of Placental Development
The placenta is a temporary but important organ. It helps bring nutrients and oxygen to the fetus, removes harmful waste, provides immune protection, and produces hormones to support fetal development. The placentas of different mammalian species vary widely and likely reflect changes during evolution.
 BACK TO TOP
BACK TO TOP