DIR provides fundamental knowledge about the nature and behavior of living systems through basic, clinical, and population-based research. Scroll through the following slideshow to learn about select scientific advances from each affinity group.

Understanding How Physical Activity During Pregnancy Impacts the Placenta
Maternal physical activity during pregnancy can benefit childhood health, but the mechanisms remain unclear. Emerging data suggest a role for placental epigenetics—heritable changes in DNA that do not involve alterations to the underlying sequence.
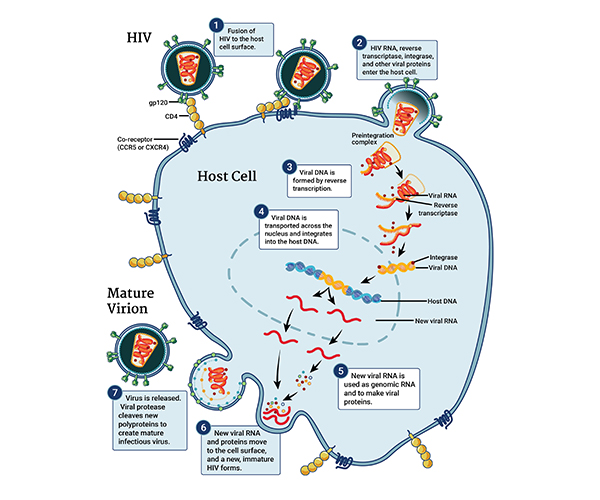
Unraveling an Alternate Mechanism of HIV Integration
When HIV infects a cell, it inserts its genetic material into the host genome, a process known to rely on the viral enzyme integrase. However, HIV and other retroviruses retain some insertion activity even in the absence of integrase. Understanding how this happens can help inform HIV treatment strategies, which now incorporate integrase-blocking drugs.
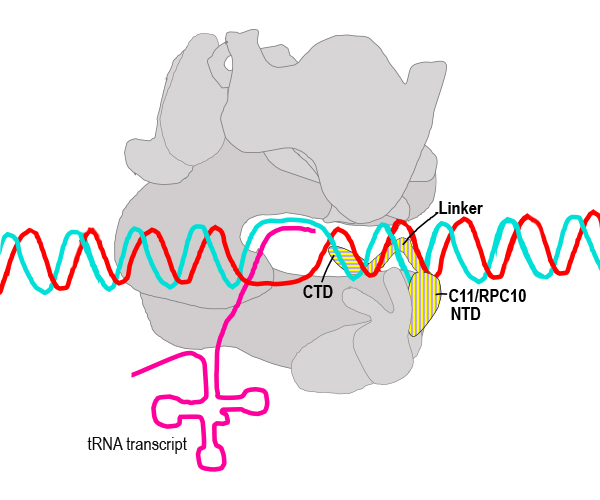
Understanding a Critical Component of RNA Polymerase III
The multisubunit nuclear RNA polymerase III (Pol III) specializes in transcribing genes that encode transfer RNAs and other non-coding RNAs. Distinct from this function, cytoplasmic Pol III plays a critical role in antiviral immunity. Scientists are studying Pol III to understand how its components work to contribute to its cellular functions.
Understanding How Neurons Sense Synapse Activity
Transmission of chemical signals through synapses is essential for information processing in the nervous system. Synapses develop and mature via tightly regulated processes that are closely linked to synaptic activity, but the mechanisms by which neurons sense synapse activity are poorly understood.
Improving Predictions of Preterm Delivery
Preterm birth is a leading cause of infant death and long-term disability related to the nervous system in the United States. Identifying pregnant women at risk for preterm delivery is essential for developing safe and effective preventive strategies.

Understanding Eating Behaviors Among Children and Adolescents
Some studies estimate that nearly a quarter of American children and adolescents experience “loss-of-control eating,” meaning they feel a lack of control over what they are eating, regardless of how much food is consumed.
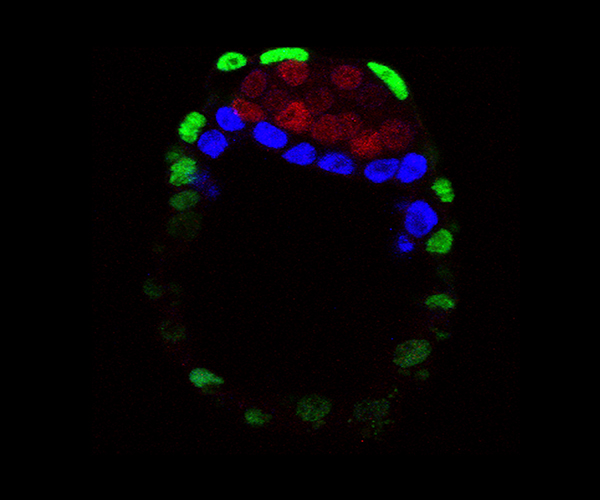
Exploring How Progenitor Cells Make Cell Fate Decisions
During embryonic development, a wide variety of cells, tissues, and organs originate from a handful of progenitor cells. These progenitor cells undergo precise programming to become a specific cell type—a process that is often called a cell fate decision.

Evaluating the Effects of Ultra-processed Food During Pregnancy
Ultra-processed foods are linked to obesity, as well as heart and metabolic diseases. However, few studies have evaluated their effects on pregnant people, including how ultra-processed food influences blood pressure, weight gain, and gestational diabetes.
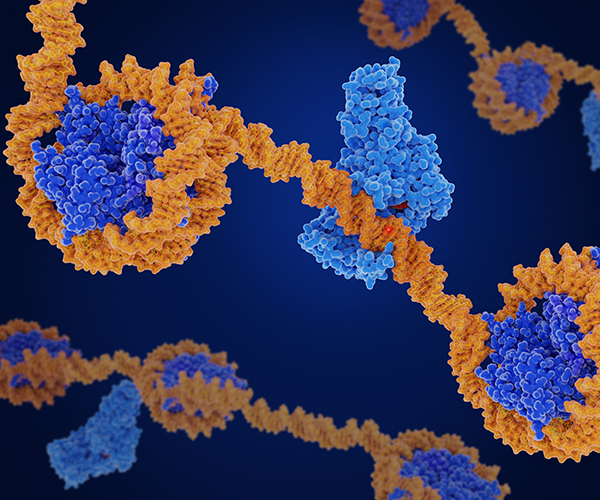
Determining How DNA is Remodeled for Transcription
Transcription refers to the process in which instructions in DNA are converted to messenger RNA, which can leave the cell’s nucleus to direct synthesis of its encoded protein. While scientists know the general steps and key factors involved in the initiation of transcription, there is still much to learn about how this process is coordinated.
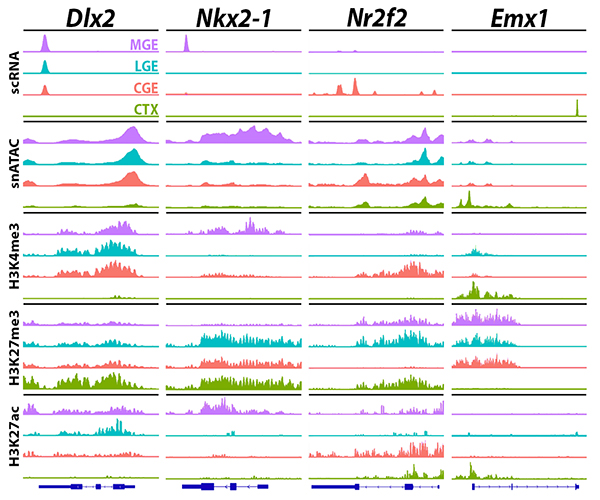
Mapping Early Neurodevelopment in the Forebrain
A thorough characterization of the mechanisms regulating neuronal fate and maturation during early embryonic development provides foundational knowledge for understanding brain function and how neurological diseases arise.
 BACK TO TOP
BACK TO TOP