
Uncovering the Cause of a Rare Skeletal Disease
Studying rare skeletal diseases can improve understanding of how bone formation is regulated.
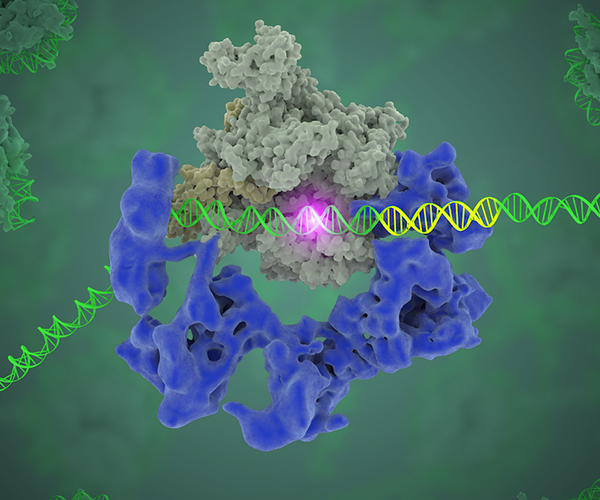
Precisely Defining Transcription Factor Binding Sites
Transcription factors control gene expression by binding to nearby DNA. Although scientists have developed techniques to identify the DNA sequence recognized by a certain transcription factor, transcription factors often bind to only a fraction of the predicted binding sites that occur in the genome.
Read about work from the Clark Lab to more precisely define transcription factor binding sites.
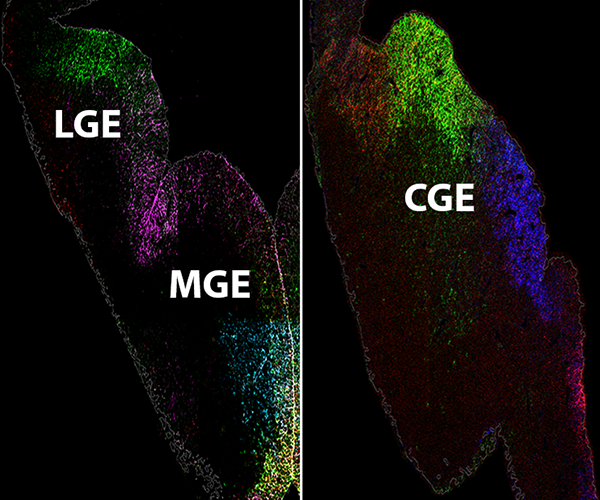
Characterizing Gene Expression Patterns in the Embryonic Brain
Inhibitory GABAergic interneurons are an incredibly diverse cell population that plays critical roles in nearly all brain activity. A better understanding of the mechanisms that regulate interneuron fate and maturation is critical to understand both normal brain development and the causes of certain neurological diseases.
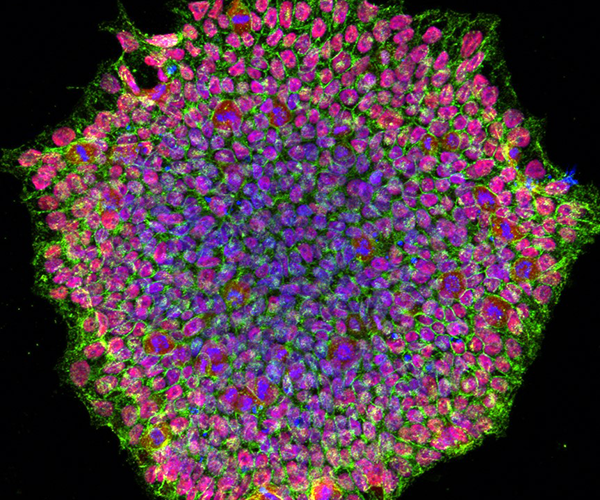
Preventing Tumors that May Arise from Stem Cell Therapies
Stem cells offer enormous promise for the field of regenerative medicine, but the risk that they may develop into tumors poses an obstacle to their clinical use.

Highlighting Health Disparities in Pregnancy
Pregnant women in the United States can face a range of health complications that are exacerbated by race and ethnicity, geography, and age. Less is known about how pregnant women with disabilities are affected.
Read about work from the Epidemiology Branch on risks specific to women with disabilities.

Identifying the Long-Term Health Effects of Pregnancy Loss
Pregnancy loss occurs when a pregnancy unexpectedly ends before the 20th week. Studies suggest that women who experience a pregnancy loss may be at higher risk for long-term health problems like heart disease.
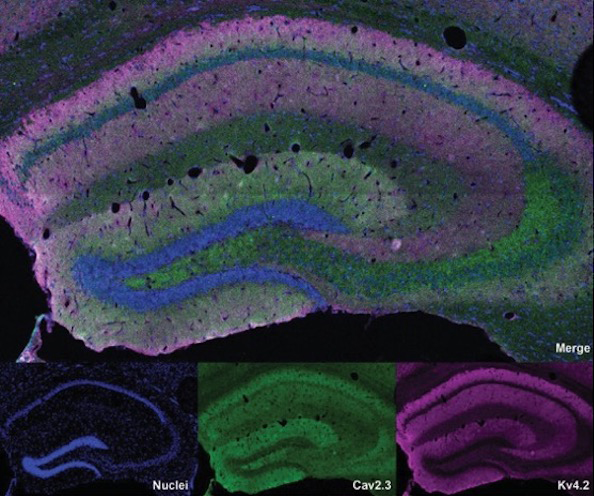
Understanding Synaptic Regulation in the Hippocampus
Neurons in the brain communicate using chemical messengers called neurotransmitters, as well as electrical signals from various types of charged ions, including calcium and potassium. Small gaps in between neurons, called synapses, serve as hubs for transmitting and regulating this information.
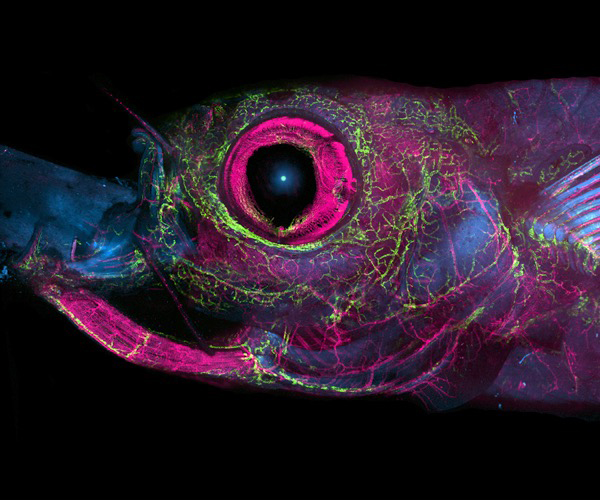

Developing Live Imaging Technologies for Researchers
Zebrafish are model organisms for a variety of scientific disciplines, including developmental biology, neuroscience, and oncology. Imaging live adult zebrafish is challenging, but NICHD researchers have developed new methods that enable long-term imaging of zebrafish and cavefish, another aquatic model used by scientists.
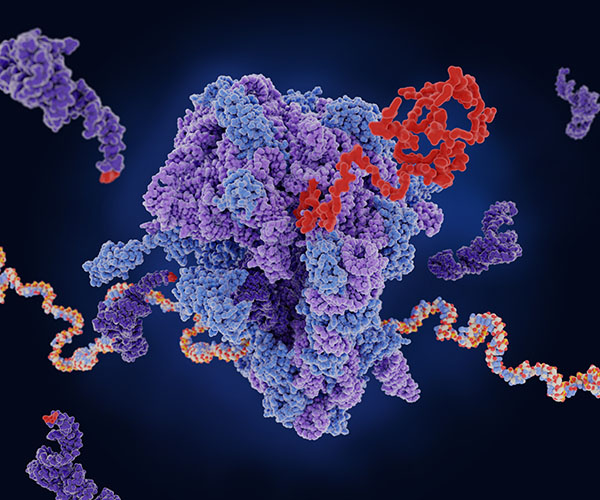
Developing Methods to Identify Disease-Causing Mutations
RNAs carry various instructions for cells. Messenger RNAs are translated into proteins, and non-coding RNAs, such as tRNAs, carry out other important functions in a cell. Mutations in enzymes that modify tRNAs lead to a variety of human diseases.
 BACK TO TOP
BACK TO TOP